r programming language linkedin assessment answers
1. Review line 1 below. What does the statement in line 2 return?
1 mylist<-list(1,2,"C",4,5)
2 unlist(mylist)
- [1] 1 2 C 4 5
- [1] “1” “2” “C” “4” “5”
- “C”
- [1] 1 2 4 5
2. Which strings could be returned by the function ls (pat="^V" )?
- VisitPCA, VarX
- Xvar, Yvar
- ANOVAData, anovadata
- VisitPCA, varx
3. Which option setting can cause difficulty if you want to add to a variable's possible values after you have designed an object's initial data structure?
- options (max.print=5)
- options (stringsAsFactors=TRUE)
- options (colnames (x) <- NULL)
- options (continue=”…”)
5. In the image below, the data frame on lines 1 through 4 is named StDf. StDf contains no factors. Why does the statement on line 6 return "character" while the statement on line 7 returns "data.frame"?
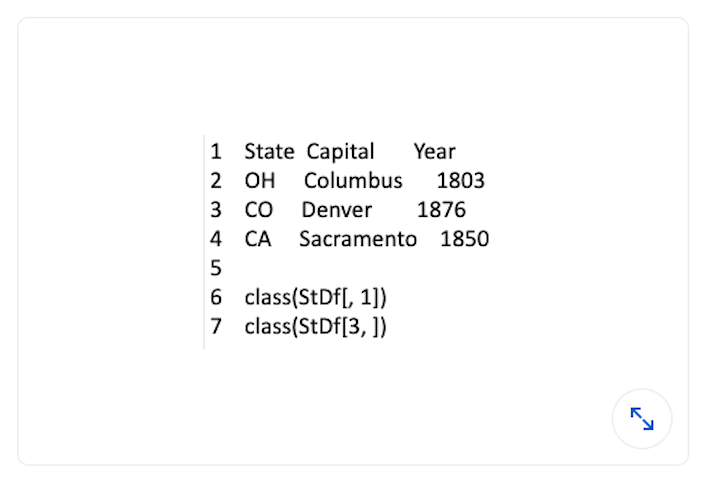
- By specifying the final row, 3, and no column specified, StDf[3,] calls for the complete structure.
- Columns in a data frame are vectors generally containing a single type of data. Rows in a data frame are lists, but they belong to a structure that has multiple rows: the data frame.
- Each value in the first column is a character value, but the values in the third row include both character and numeric values.
- Each value in the first row is a character value, but the values in the third column include both character and numeric values.
6. The variable potus is a character vector, as shown in line 1 below. Which statement returns the results shown?

- potus[1:2 4]
- potus[-3]
- potus[1,2,4]
- potus[-“GW Bush” ]
7. Review line 1. What does the statement on line 3 return?
1 mtrx <- matrix(1:6, 3, 2)
2
3 mtrx[, -1]
8. What does the function power. anova. test return?
- the probability of making a Type Il error
- the probability of not making a Type Il error
- the probability of not making a Type I error
- the probability of making a Type I error
9. How do you get documentation of an installed and loaded R package named dplyr and packages with dplyr as an alias?
- ? dplyr
- Press the F1 key.
- help(dplyr)
- ?? dplyr
10. × is a vector of type integer, as shown in line 1 below. What is the type of the result returned by the statement > median (x)?
1 x <- c (12L, 6L,10L, 8L,15L,14L,19L,18L, 23L, 59L)
- integer
- single
- double
- numeric
11. You have data on the degree of approval for a ballot measure from Democrats, Republicans, and Independents. To test the statistical significance of the difference between any of the party means, which R function should you use?
- t.test {stats}
- power.t.test {stats}
- TestA {DescTools}
- anova.lm {stats}
12. d. pizza is a data frame. Its column named temperature contains only numbers. If you extract temperature using the [1 accessors, its class defaults to numeric. How can you access temperature so that it retains the class of data. frame?
> class( d.pizzal[ , "temperature" ] )
> "numeric"
- class( d.pizza[ , “temperature”, drop=F ] )
- class( d.pizza$temperature )
- class( d.pizza[ , “temperature”] )
- class( d.pizza( , “temperature”) )
13. Why does sum(!is.na(pizzaSweek) ) return the number of rows with valid, non-NA values in the column named week?
- !is.na (pizza$week) returns a vector of TRUE/FALSE values, in which TRUE is treated as a 0 and FALSE as a 1.
- !is.na (pizza$week) counts the number of NA values in the column.
- The exclamation point in !is.na (pizza$week) reverses the meaning of the test it precedes.
- !is.na (pizza$week) counts the number of non-missing values in the column.
14. How do you obtain the row numbers in a data frame named pizza for which the value of pizza$delivery min is greater than or equal to 30?
15. ournames is a character vector. What values does the statement below return to Cpeople?
Cpeople
<-
ournames %in% grep("^C", ournames, value =
TRUE)
- TRUE or FALSE, depending on whether any character in ournames is C
- records where the first character is a C
- TRUE and FALSE values, depending on whether the first character in an ournames record is C
- any record with a value containing a C